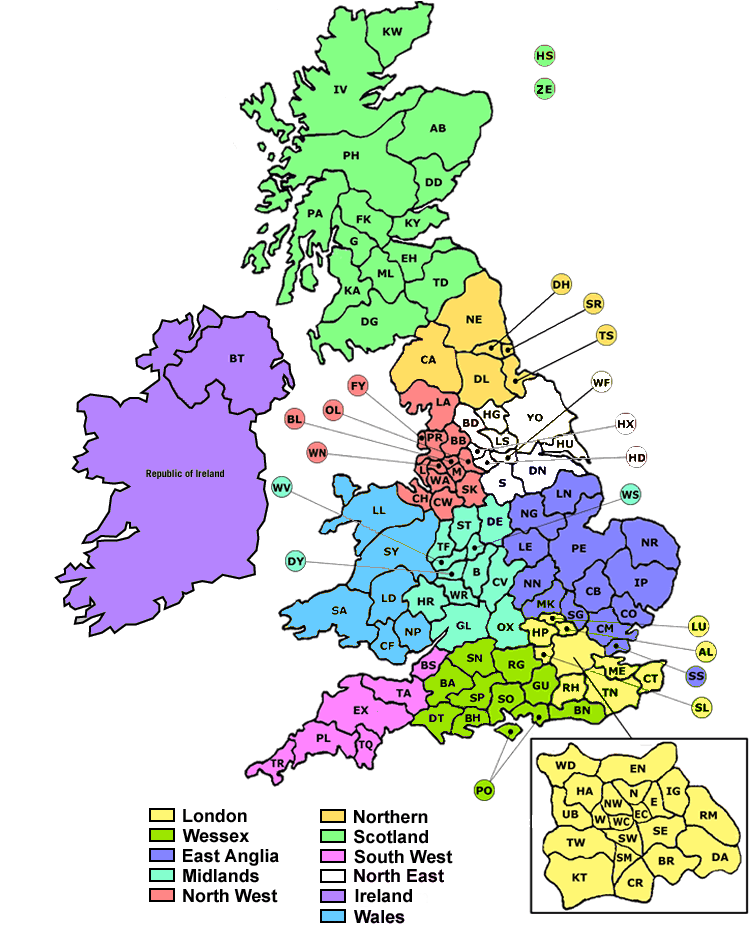
The structure of a postcode is two alphanumeric codes and are variable in length: ranging from six to eight characters (including a space). Each postcode is divided into two parts separated by a single space: the outward code and the inward code respectively. The outward code includes the postcode area and the postcode district, respectively. The inward code includes the postcode sector and the postcode unit respectively.
for example, the postcode BD21 2RQ denotes,
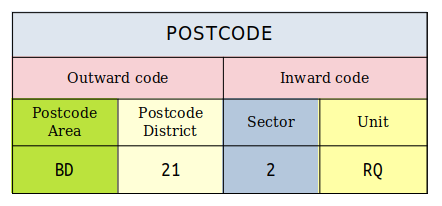
Outward code
The outward code is the part of the postcode before the single space in the middle. It is between two and four characters long.
Postcode area
The postcode area is part of the outward code. The postcode area is either one or two characters long and is alphabetical.
This is the largest geographical unit of the postcode. Each one comprises one or two alphacharacters generally chosen to be a mnemonic of the area. Examples of postcode areas are MK for Milton Keynes, SO for Southampton, "L" for Liverpool, "RH" for Redhill and "EH" for Edinburgh. A postal area may cover a wide area, for example "RH" also covers parts of north Sussex and "BT" (Belfast) covers the whole of Northern Ireland.
Postcode district
The postcode district is one digit, two digits or a digit followed by a letter. Each postcode area is divided into a number of districts which are represented by the numerical portion of each part of the postcode. These numbers range from 0 to 99 eg MK42. In London a further alphacharacter is used to divide some districts into sub divisions eg EC1A.
Inward code
The inward code is the part of the postcode after the single space in the middle. It is three characters long. The inward code assists in the delivery of post within a postal district.
Postcode sector
The postcode sector is made up of a single digit (the first character of the inward code). Postcode Sectors are numbered 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,0. It should be noted that when sorting postcodes into order, sector 0 is the tenth sector rather than the first.
Postcode unit
The postcode unit is two characters added to the end of the postcode sector. A postcode unit generally represents
- a street, part of a street
- a single address
- a group of properties
- a single property
- a sub-section of the property
- an individual organisation or (for instance Driver and Vehicle Licensing Agency) a subsection of the organisation